GTM Infra: The Missing Piece in Healthcare Ops
The Quiet Revolution: Why GTM Infra is the Missing Piece in Healthcare Ops
Beyond the CRM: Why the Next Wave of GTM Innovation Starts With the Data Layer
The best GTM strategies don’t start with a sales deck, they start with clean, accessible data.
If you’ve ever read a RevOps playbook and thought, “This is great, but what about clinical operations? What about providers trying to stand up care programs on the fly, in a regulated minefield, using duct-taped tools from 2006?”—you’re not alone.
The latest post from The Signal, "The Platform Democratizing GTM Engineering", nails something we’ve believed for a long time at CareLaunch: GTM is no longer just about marketing and sales. It’s about execution at scale, and that starts with infrastructure.
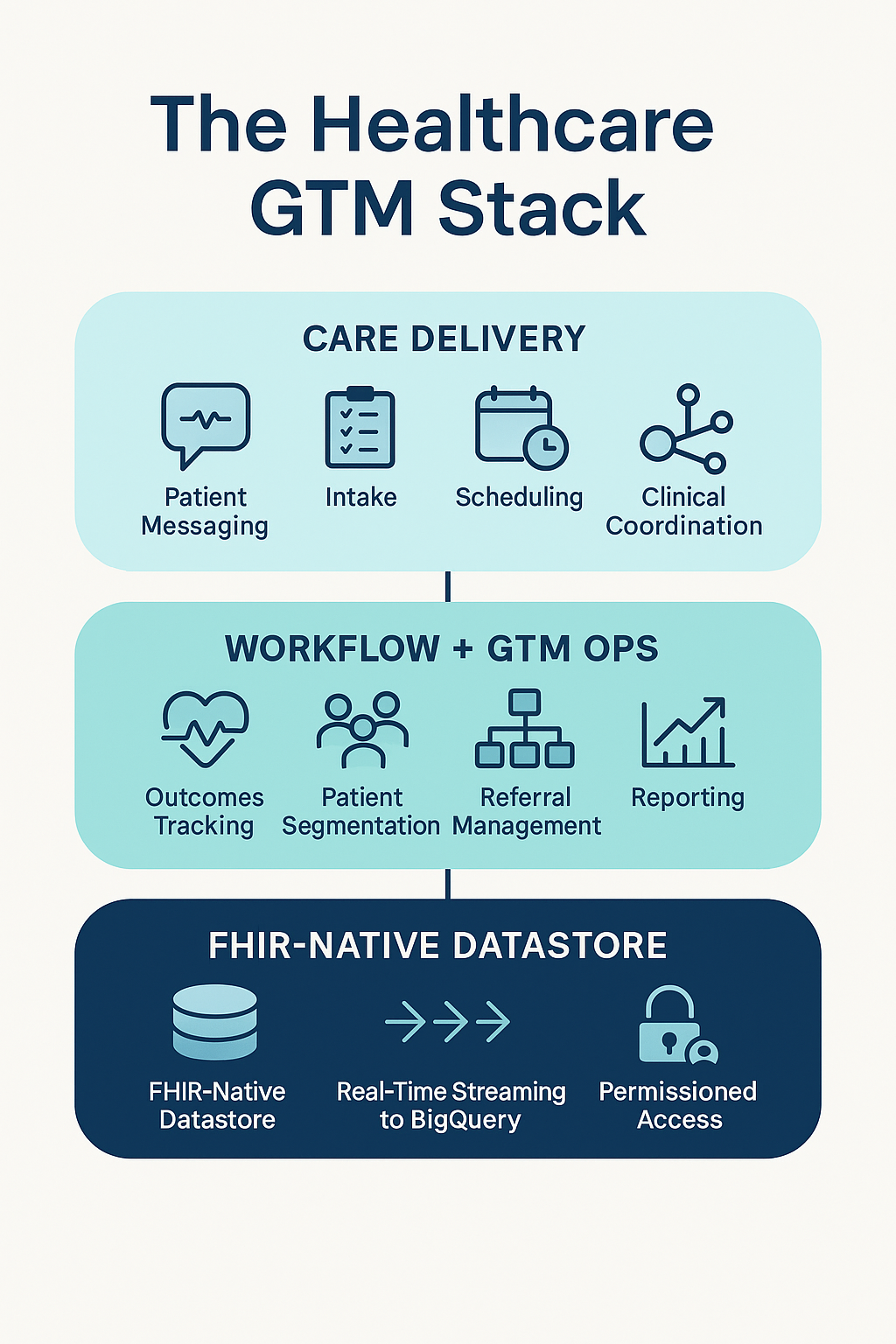
At CareLaunch, we call this the foundational data layer for care delivery. But if you squint, it’s really just healthcare’s version of GTM infra.
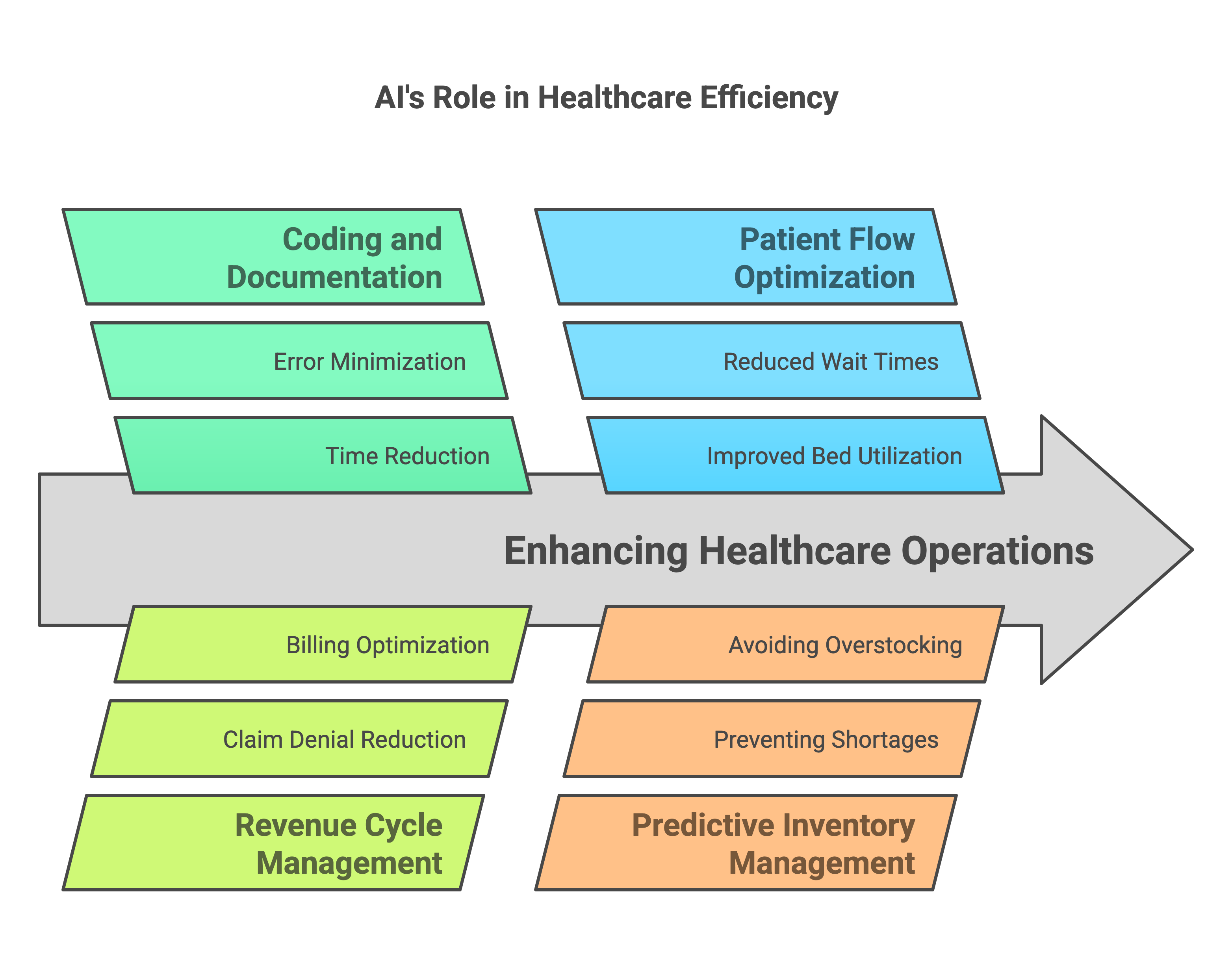
1. From Sales Ops to Care Ops: Same Bottlenecks, New Stakes
Traditional GTM teams struggle to move quickly because data lives in silos, tooling requires engineering support, and processes are too brittle to adapt mid-launch.
Sound familiar?
Healthcare orgs especially digital health startups and multi site provider groups face the same challenges, but with higher stakes. Instead of missed leads, it’s missed follow-ups. Instead of lost MRR, it’s dropped patients. Instead of poor sales attribution, it’s poor outcomes tracking.
That’s why we built CareLaunch to be more than a CRM. It’s a composable platform that sits at the center of care coordination, patient communications, outcomes measurement and yes, growth.
2. Why “GTM Infra” Isn’t Just for SaaS
Platforms like Common Paper and Retool are changing how non-technical teams launch, iterate, and optimize. They’ve cracked the code by giving go-to-market teams access to developer-grade tools without the overhead.
CareLaunch is doing the same, but for healthcare.
Need to spin up a new intake flow? Launch a self-pay offering? Send an outcomes survey based on a FHIR encounter? You don’t need six tools and a sprint cycle. You need the ability to build in the flow of work. And you need data you can trust, structured and ready for use across every part of your business.
3. Data as Leverage, Not Liability
You’ve heard the interoperability promise before: “integrated,” “connected,” “talking systems.”
Too often, that just means more complicated interfaces.
We went the other way. CareLaunch is FHIR-native, built on a composable architecture that streams structured data (in real-time) to BigQuery. No glue code. No data silos.
This matters more than it sounds. Because this isn’t just CRM data. We’re talking:
- Clinical observations
- PROs and patient adherence
- Resource utilization
- Health economic endpoints
- Signals across intake, messaging, and care coordination
When you structure this natively, you unlock next level GTM: signal stacking, async models, outcomes based workflows, and analytics that cross the aisle—from clinical to commercial.
4. Move Fast. Stay Compliant. Scale Intelligently.
We didn’t just wrap a pretty UI around clunky EHR infrastructure. We built a care first GTM engine that’s HIPAA compliant, composable, and ready to scale.
That means:
- No waiting on your dev team to launch a new service line
- No more vendor Frankenstack to glue together chat, intake, scheduling, and reporting
- No more flying blind on what’s working or not in your funnel
You can go from MVP to multi-state rollout with a platform that flexes as you do.
The TL;DR
If you’re building in healthcare and care delivery is your product, then GTM isn’t a downstream afterthought, it’s baked into everything you do.
CareLaunch gives you the infrastructure to move like a SaaS company and scale like a system. One platform, every patient touchpoint, all in one place.
Want to see what healthcare GTM infra actually looks like in practice?
Book a demo—or better yet, start building.